In an increasingly wireless world, the need for highly optimized WiFi connections is universal. From personal home networks to expansive networking topologies deployed by the largest companies—WiFi signal strength is paramount for a good internet experience. If you suspect that weak WiFi signals are a problem in your network, measuring WiFi signal strength can confirm any issues
To understand if your network issues are related to spotty signals, there are a few fundamental elements that need to be addressed. The first is understanding what constitutes a good WiFi signal, so you have a baseline measurement. The next step in the process is to measure WiFi signal strength to confirm the issue. Then—armed with that data—you can implement the best solution to increase the overall signal strength.
What is Considered a Good WiFi Signal Strength
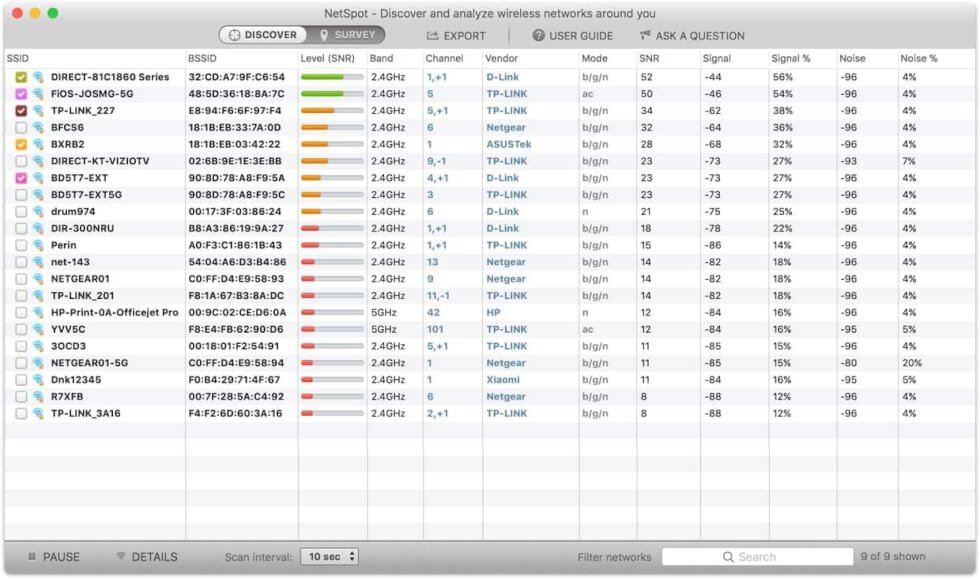
Good WiFi strength can be relatively subjective. What may be considered a great signal by one party might not be good enough for someone else. Despite this, there are generally accepted WiFi signal ranges indicating if you have poor or good signal strength.
Before jumping into these specific ranges, one note is that when measuring WiFi signal strength, the most commonly used units are dBm (decibel milliwatts), and they are expressed in negative values.
Maximum Signal Strength – -30 dBm
A reading of -30 dBm after measuring your WiFi Signal is the strongest signal your wireless hotspot will emmit. This is useful to know because when you are measuring your WiFi signal strength, you can place your measurement device right next to the access point to establish that it is emitting properly.
Excellent Signal Strength – -50 dBm
Measuring WiFi signal strength in the -50 dBm range is considered excellent signal quality and is useful for all internet activities.
Good Signal Strength – -60 dBm
A reading of -60 dBm indicates a good signal with great reliability characteristics. If you are having WiFi issues and you measure WiFi signal strength of -60 dBm, they are likely not related to signal strength.
Ok Signal Strength – -67 dBm
Measuring WiFi signal strength and discovering a reading of -67 dBm means that you have okay signal quality. This is the bare minimum for a good internet experience, but there is room for improvement.
Poor Signal Strength – <-70 dBm
If you measure WiFi signal strength of less than -70 dBm, then improvements are necessary to maintain network stability. Discovering a signal in this range means that working to improve the signal strength will provide a more reliable and useful signal.
How To Measure WiFi Signal Strength
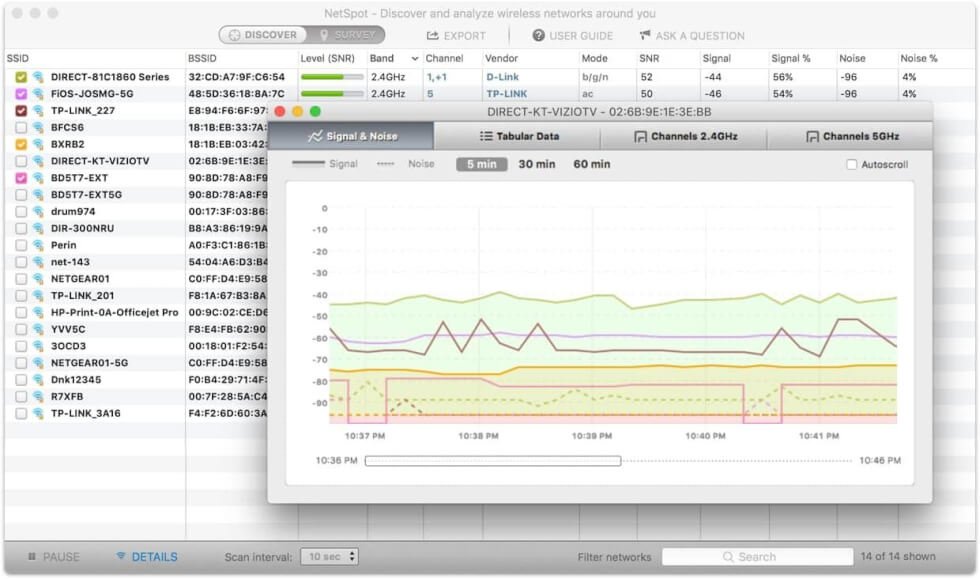
Now that you are able to interpret what signal measurements mean, it’s time to perform a WiFi site survey. This survey will measure different points within your service area to determine if your signal strength is adequate for your needs. There are many commercially available tools for measuring WiFi signal strength, but NetSpot is a robust and well-rounded option.
Users who choose to measure WiFi signal strength with the help of NetSpot can try some of the application’s functionalities for free. Later, if they decide to use some of the more advanced functionalities, there are different plans price depending on your needs. The app does more than measure WiFi signal and perform site surveys. It can also be instrumental in planning your network and troubleshooting other issues you might be experiencing.
Of course, no matter what tool you decide to use, the important part is to measure WiFi signal strength in a variety of areas and record the results. After testing locations at various distances and elevations from the access point, you can identify areas where your WiFi signal is weak and begin implementing solutions for peak performance.
How To Increase WiFi Signal Strength
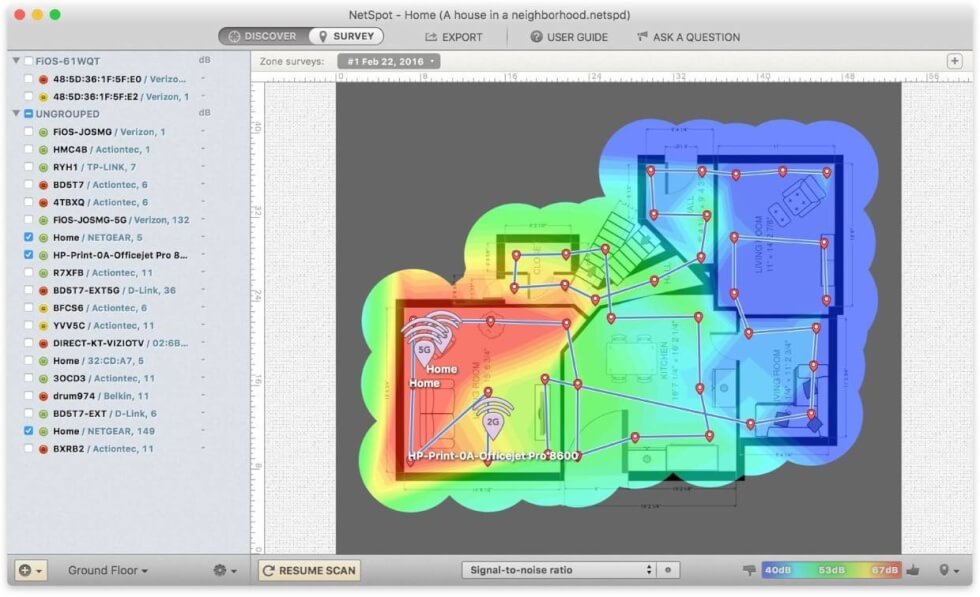
Now that you understand the areas of your network with poor WiFi signal—and after measuring WiFi signal strength —there are many methods that can signal quality. Here are a few you can leverage to ensure the best wireless networking performance.
Checking Access Point Location
Many devices in your home can cause interference that will potentially crush signal strength. Examples of such devices include cordless phones, appliances, and televisions. If your access point is near any of these things, you should try to select a more suitable location— and then measure WiFi signal strength again.
Check Your Channel
If your access point is free of any devices that cause interference—or if you discover weak signal after measuring your WiFi signal strength —another option is adjusting the channel of your router.
Many devices operate within the same frequency range as your access point. These devices are not limited to your own home either and include other routers on other networks. To make sure your router has enough room on its channel to communicate, you should check and make sure it is not too congested.
If you utilize NetSpot when performing your WiFi site survey to measure your WiFi signal strength, you can also perform a channel analysis to determine the optimal selection for your access point. Without a tool that can measure transmission channels of other devices, your best bets are channels 1,6, or 11.
Check Your Access Point’s Coverage Area
If none of the above methods work to increase your results when you measure WiFi signal strength, your next step is to check the range of your access point. Every wireless access point has different transmission capabilities, and the weak signal may be occurring because your current access point cannot reach your desired coverage area.
To fix this issue, you may need to upgrade to an access point with a more powerful antenna they can transmit over a longer distance. You can also upgrade your router to the latest standard if you haven’t done so already. And another step you can take is to place a wireless repeater or bridge to gap the distance. After doing this, you can measure your WiFi signal strength again and check for improvements.
Good WiFi Strength is Possible for Everyone
If you are frustrated with patchy connections and suspect the cause is due to poor signal strength, you can quickly test for this problem. Understanding what a good WiFi signal is, and then measuring WiFi signal strength —with powerful tools such as NetSpot—you can confirm and identify any problem areas. Creating a better, stronger WiFi signal all starts by measuring WiFi signal strength.







